Introducing TFree-HAT 7B: Tokenizer-Free Models Achieving Top-Tier Multilingual Performance
We’re excited to share something fresh from our research lab. For the bigger picture on why we’re building tokenizer-free models in the first place, check out more background here.
Just recently, we made public two new tokenizer-free models built on our Hierarchical Autoregressive Transformer (HAT) architecture:
- TFree-HAT-Pretrained-7B-Base, pre-trained from scratch in English and German
- Llama-TFree-HAT-Pretrained-7B-DPO, a post-trained model building upon the base version
These models build upon previous work released in April, where a Llama 3.1 8B backbone was retrofitted with the HAT architecture. With these 7B models, we successfully trained the HAT architecture end-to-end, further establishing it as an architectural advancement in how models can process and understand text.
At their 7B scale, they were built to work under deployment constraints, such as in on-device processing, local deployment or other tasks requiring efficient text compression.
These models deliver:
- Exceptional German-language performance in this size class, outperforming Llama 3.1 8B in 67% of measured German benchmarks, while matching performance in English.
- Excelling in LLM-as-a-judge settings: answers from the 7B-DPO model are preferred over those from Llama 3.1 8B in 69% of English cases and 75% of German cases.
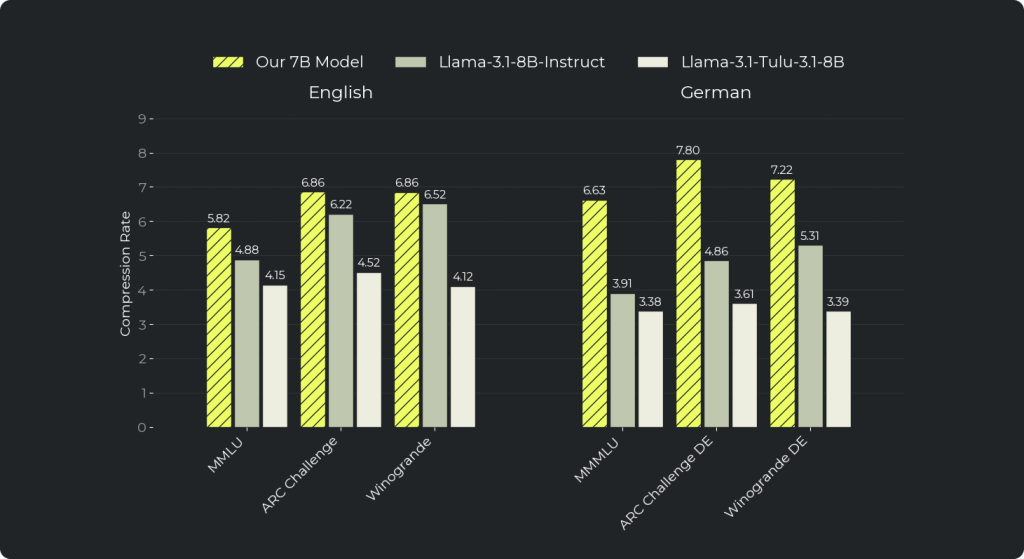
- Better sequence compression: HAT processes language in full words rather than in the smaller subword pieces, which allows HAT to understand the same text using fewer steps (i.e., a higher compression rate). This higher compression rate provides opportunities for more efficient inference, e.g., it reduces FLOPs in German by 40% compared to a baseline.
Translating these reduced FLOPs into improved actual throughput/latency depends significantly on the inference implementation and hardware. To enable the community to research and develop with T-Free, we are open-sourcing a work-in-progress (forked) vLLM implementation that supports T-Free models, in which relevant metrics like latency and throughput can be measured.
We have additionally released 200 pre-training checkpoints over training for future study and use by the community, e.g., to study learning dynamics, which can be found in the model card of the base model.
Below, we outline what makes TFree-HAT special, how it performs and how you can start building with it today.
Side note: The DPO model was fine-tuned using Llama 3.3 for filtering. In line with the Llama license, we’ve named the model with the llama prefix.
Why Tokenizer-Free?
Tokenization, i.e., how we split text into pieces (subword vocabulary), often favors English, so other languages and scripts get chopped into many tiny parts. In low-resource languages and niche domains (e.g., law, manufacturing), common terms are split into rare subpieces, making sequences longer, compute cost higher and the meaning fuzzier. This fragmentation hurts learning and generation quality. Net result: built-in language and domain bias that makes LLMs less efficient, more expensive and less reliable where data is scarce.
Our architecture replaces the large, fixed subword vocabulary with a byte-level encoder and decoder wrapped around a word-level backbone. This design reduces the total parameter count from 8B to just under 7B by shrinking both the embedding and language model head matrices. Because bytes are universal, the model adapts smoothly to new languages and domains without the issues caused by tokenization laid out above.
We measure these efficiency gains using compression rate, the average number of bytes represented per sequence position. A higher rate means the model processes more text in fewer steps, directly translating into lower compute requirements. The advantage of HAT over standard tokenization becomes most visible in low-resource languages and specialized domains, where traditional tokenizers break text into disproportionately small pieces. In our evaluations, HAT achieved on average 40% better compression in German and 16% better compression in English compared to Llama 3.1 8B , demonstrating both its ability to handle challenging languages efficiently and to outperform in high-resource settings as well.
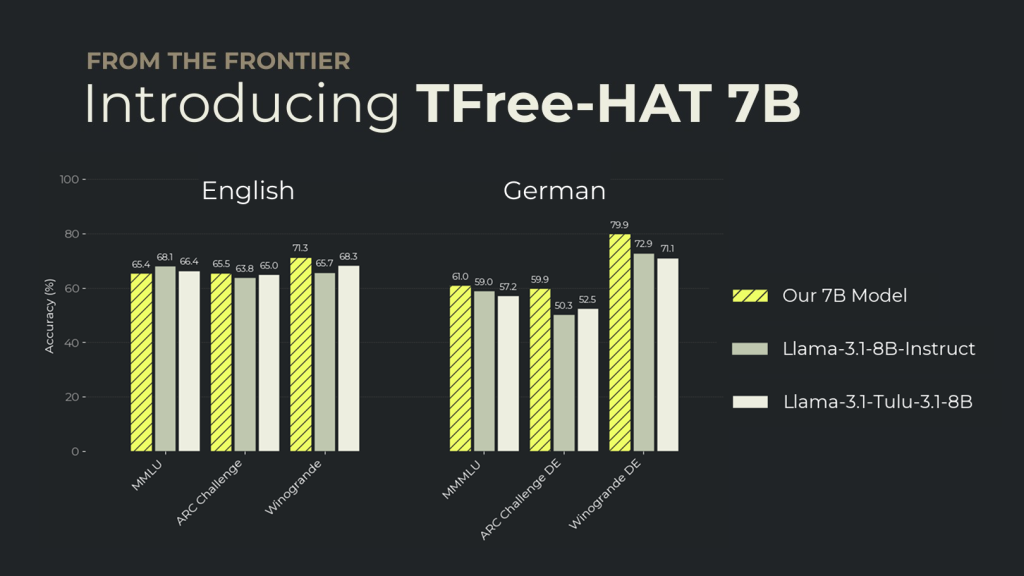
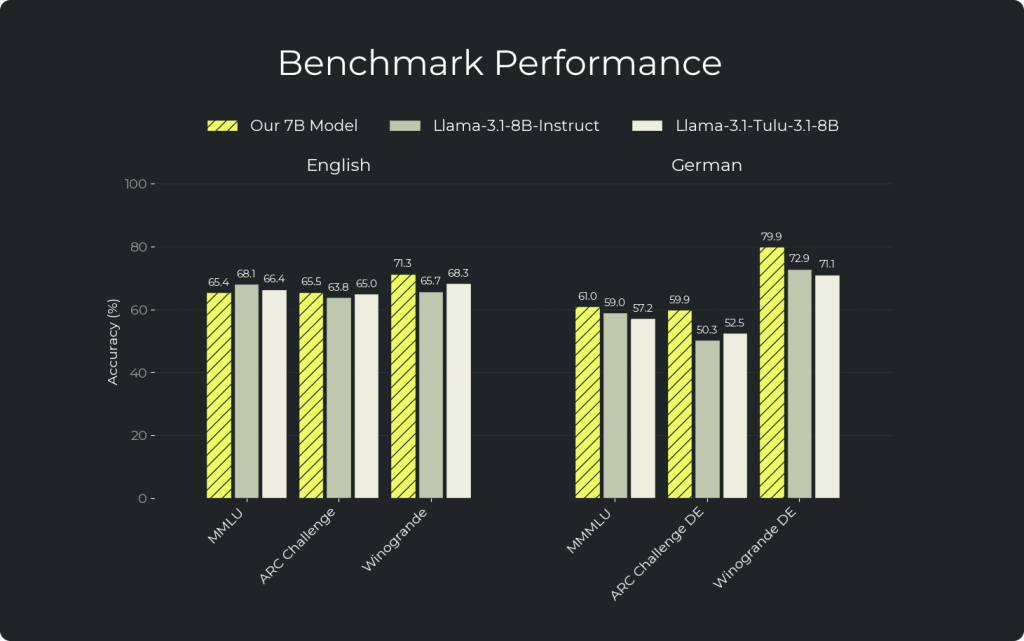
Benchmarks
We evaluate all models using the same harness and settings to ensure apples-to-apples fairness. We compared our DPO model to Llama 3.1 8B Instruct and Llama Tulu 3.1 8B across a total of 28 English & German benchmarks. Full evaluation results are available in the corresponding model cards: Base evaluations, DPO evaluations.
Numbers are based on the DPO model.
The results show that our DPO model outperforms Llama 3.1 7B Instruct on 67% of German benchmarks, while being on-par in English.
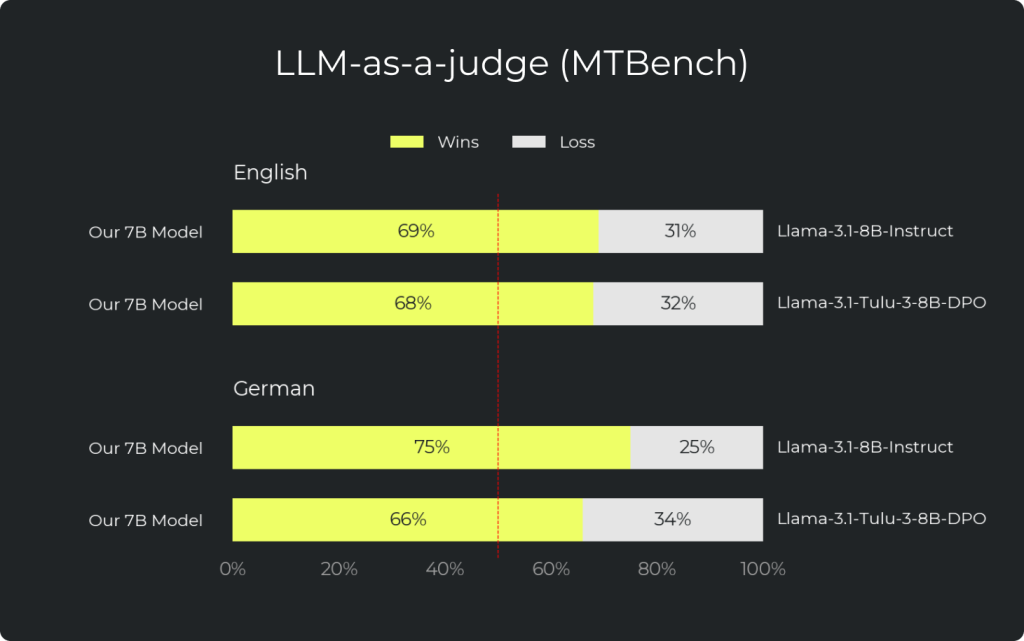
LLM-as-a-Judge (MTBench)
Our models show strong performance on MTBench, a benchmark built using FastChat to evaluate model helpfulness through pairwise comparisons. In these evaluations, answers from the 7B-DPO model are preferred over those from Llama 3.1 8B in 69% of English cases and 75% of German cases.
Get Started
In order to make these models accessible, we provide two inference implementations: Hugging Face and vLLM. The following section describes how to get our models up and running. Note that Hugging Face is mostly intended for testing purposes, while vLLM is a high-performance inference implementation, making better use of the HAT architecture.
Hugging Face
Weights and safetensors:
We provide an inference module compatible with Hugging Face Transformers. For best results, we recommend pinning the Transformers library to version 4.46.3. Before running the example below, make sure the hat-splitter package is installed in your environment.
pip install 'hat-splitter>=0.1.9' 'transformers==4.46.3' torch
pip install flash_attn
Download model weights and run inference using the following example:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
INPUT ="When was Rome founded?"
MODEL_ID = "Aleph-Alpha/Llama-TFree-HAT-Pretrained-7B-DPO"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
trust_remote_code=True,
pretrained_model_name_or_path=MODEL_ID,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
).to("cuda", torch.bfloat16)
input_ids, cumulative_word_lengths = model._prepare_input(INPUT, add_llama_template=True)
model_output = model.generate(
input_ids,
cumulative_seq_lengths_per_word=cumulative_word_lengths,
max_new_tokens=300,
use_cache=False,
)
print("Prompt: ", INPUT)
print("Completion: ", model_output.completion_text)vLLM Fork
A high-performance inference implementation is available on Aleph Alpha’s vLLM fork. This implementation is optimized for batched inference. Please note that it is still under active development.
1. Prerequisites
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU, minimum 20 GB VRAM
- Python: 3.12.
2. Clone and install
git clone https://github.com/Aleph-Alpha/vllm vllm-hat
cd vllm-hat
# Create and activate a 3.12 virtual env
uv venv -p 3.12
source .venv/bin/activate
# Tell vLLM to skip local compilation and use prebuilt CUDA wheels
export VLLM_USE_PRECOMPILED=1
# Finally, install in editable mode
uv pip install -eBoth checkpoints ship under the Open Aleph License for research and educational use. Try our models out today. We’d love to hear what you think.